In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, industries worldwide are embracing innovative smart manufacturing solutions to optimize production processes, enhance efficiency, and stay ahead of the curve. Join us as we explore the transformative potential of emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics in revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape.
What Is Smart Manufacturing
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines smart manufacturing as fully integrated, collaborative manufacturing systems that dynamically respond to changing demands and conditions within the factory, supply network, and customer requirements in real-time.
Smart manufacturing relies on cloud connectivity, blending human ingenuity with digitally connected machines and assets, as well as AI-powered systems and analytics. The incorporation of AI and intelligent tools enhances flexibility and accelerates the ability to tailor outputs based on real-time data and insights. The transparency, flexibility, and robustness of smart manufacturing make it a fundamental element of more streamlined supply chain models and overall business operations.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing

Improved productivity: Interconnected autonomous machines generate extensive data, facilitating real-time insights into production processes that enable managers to optimize efficiency planning and boost productivity.
Enhanced employee satisfaction: Access to cutting-edge technology attracts and retains talent while reducing human error, resulting in fewer customer dissatisfaction issues for employees to address.
Energy efficiency: All manufacturers can reduce their carbon footprint by minimizing waste, but energy-intensive industries stand to benefit most from energy savings, which not only reduce energy waste but also contribute to product affordability.
Cost-effective maintenance through predictive analysis: Smart factories leverage predictive maintenance to anticipate and address maintenance issues swiftly, mitigating costly equipment repairs and preventing production interruptions.
Enhanced customer satisfaction: Smart manufacturing empowers managers with precise data analysis, enabling efficient measurement of key performance indicators and agile response to customer needs in real time, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
Substantial cost savings: Enhanced access to supply chain and production data, coupled with advanced analytics, enhances forecast accuracy and minimizes waste, leading to cost reductions through effective demand management.
Improved quality: Digitizing processes minimizes the potential for human error and system failures, enabling real-time monitoring of processes and performance to enhance yield and optimize resource utilization.
Smart Manufacturing-Related Technologies and Solutions
Integrating smart manufacturing solutions into traditional manufacturing practices enables precise forecasting of needs, and error detection, and streamlines innovation within the manufacturing process.
Several technologies play important roles in adopting a smart manufacturing approach, including data lakehouse solutions, integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), analytics driven by AI/machine learning, digital twins, as well as augmented reality and robotics.
Cloud computing

Cloud computing provides manufacturers with immediate access to system resources like IIoT data, analytics, and process automation through wireless channels such as Wi-Fi or 5G. These resources are available on demand and can be accessed from centralized yet distributed large clouds across regional or global locations.
Read more: Stagnate Or Innovate: A Deep Dive Into Asia Technology Outlook & Strategic Imperatives
Data Lakehouse

A data lakehouse represents a contemporary, open framework that empowers manufacturers to store, interpret, and analyze diverse data types. It combines the power and depth of data warehouses with the flexibility of open-source data technologies commonly used by manufacturers today.
Access to powerful solutions for real-time collection and aggregation of operational data, extracting insights from this data, facilitating rapid communication, and fostering decision-making processes are all important elements of an effective decision-making framework.
A use case involves helping manufacturers achieve supply chain resilience by enhancing their capacity to source from various suppliers. A data lakehouse facilitates this by enabling the integration of data from the ERP system, managing order processes, down to the inventory, warehouse management, and transportation systems responsible for the delivery of materials essential for production.
AI/ Machine Learning

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) represent two types of intelligent software solutions that are revolutionizing the technology landscape, aiming to mimic human-like capabilities.
Fundamentally, AI is a technology solution that replicate human intelligence to execute tasks while continuously refining its performance based on gathered information.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, focuses on constructing software systems capable of learning and enhancing performance through data analysis. Consequently, every machine learning solution qualifies as an AI solution, although not all AI solutions incorporate machine learning components.
In manufacturing, machine learning is important in uncovering underlying causes of quality, yield, and operational issues. Experts can leverage profound insights to expedite decision-making and alleviate production bottlenecks.
Smart manufacturing solutions leverage both artificial intelligence and machine learning to contextualize data and furnish actionable insights, facilitating predictive maintenance to preemptively address machine failures, adjust production schedules, and mitigate costly downtimes.
Manufacturers can streamline various internal processes—such as inventory management, document processing, or productivity and efficiency analysis—through automation, enabling swift responses to trends and enhancing overall quality standards.
Industrial Internet of Things
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is essential for effectively adopting smart manufacturing strategies and achieving business objectives with efficiency. A case in point is its application in a connected factory, where it facilitates the collection of live data from various sources such as equipment sensors, cameras, production robots, and other smart devices interconnected via a local 5G network.
This data is then pushed into an AI or machine learning system, which offers insights for making informed decisions regarding predictive maintenance, remote monitoring of production assets, optimizing asset usage, and automating different processes and tasks.
Anomaly Detection

Anomaly detection solutions are used for predictive maintenance in manufacturing equipment. Using prebuilt algorithms, anomaly detection identifies various deviations in time series data, automating manufacturing processes, tasks, and decisions such as equipment servicing, procurement of replacements or supplies, and predictive measures to prevent disruptions and enhance efficiency.
Efficiency monitoring in factories involves predictive analytics and the integration of diverse data sources to identify any irregular production behaviour. Employing a machine-monitoring platform aids in detecting and forecasting unusual equipment behaviors, and recommending and automating optimal actions to fix anticipated failures.
Implementing quality monitoring across the production cycle facilitates the detection of deviations in quality and the generation of predictive alerts. This enables immediate root cause analysis to pinpoint the origins of quality issues and establishes best practices training using real data derived from past quality incidents.
An Example of Smart Manufacturing
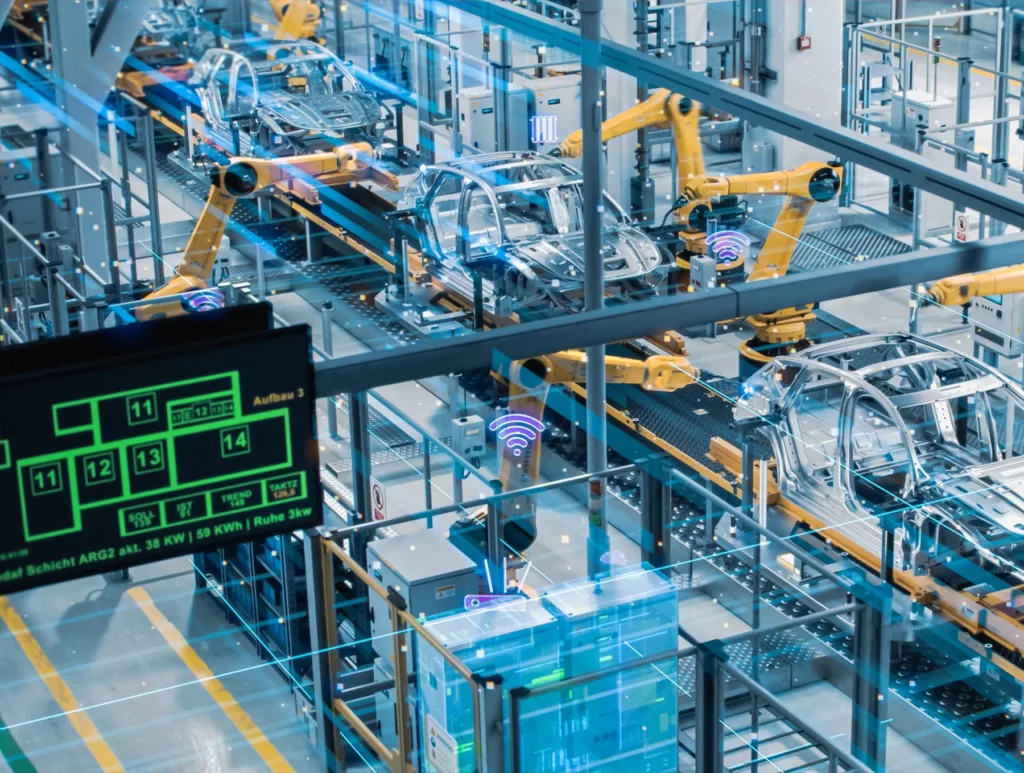

The Connected Factory in Blaichach is known as Bosch’s flagship manufacturing facility for automotive components. This facility is renowned for its production of various safety systems, including electronic stability programs (ESP) and anti-lock braking systems (ABS).
Cutting-edge technologies are used throughout the manufacturing processes. Daily operations involve the use of tablets for part inspections, machine monitoring, and process tracking, capturing quality data that might otherwise be overlooked by individual machine operators.
Furthermore, the Bosch Connected Factory incorporates a performance tracking system that promptly identifies any deviations in cycle times. This enables operators to react swiftly, intervening or correcting any issues at their nascent stages.
The Blaichach Connected Factory also implements Nexeed, a software suite crafted by the connected industry cluster to streamline production operations. This software harnesses data from over 60,000 sensors, delivering timely insights to relevant stakeholders. As a result, the team can effectively monitor all manufacturing processes and conduct predictive maintenance.
Consider Working With An Experienced Partner In Smart Manufacturing
Cooperating with CMC Global to develop smart manufacturing solutions presents an exciting opportunity to revolutionize industrial processes. CMC Global, renowned for its expertise in technology and innovation, brings a wealth of experience in implementing cutting-edge solutions tailored to various industries. Together, our collaboration aims to harness the power of emerging technologies like Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics to optimize manufacturing operations.
Contact us for further details!





