Telemedicine Technologies: Powering Remote Healthcare Services
In recent years, telemedicine has experienced significant growth and investment, propelling the telehealth market to new heights. With a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.1%, the market is set to reach an astounding $636.38 billion by 2028, up from $90.74 billion in 2021.
This exponential growth is driven by the increasing world population, the need for expanded healthcare access, the scarcity of physicians, advancements in telecommunications, and the urgent demand for remote healthcare solutions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
But how is the telemedicine technology concept revolutionizing the healthcare sector? Read on to find out.
What is Telemedicine Technology?
Telemedicine is a health-related service with the help of telecommunicating and electronic information technologies. It refers to the whole collection of deliverables designed to enable patients and their physicians or healthcare providers. It has a wide range of uses, including online patient consultations, remote control, telehealth nursing, and remote physical and psychiatry rehabilitation. It allows better health care choices, increases emergency service quality and performance, reduces time in making a diagnosis, and saves costs for both doctors and patients by optimising clinical procedures and reducing travel expenses to hospitals.
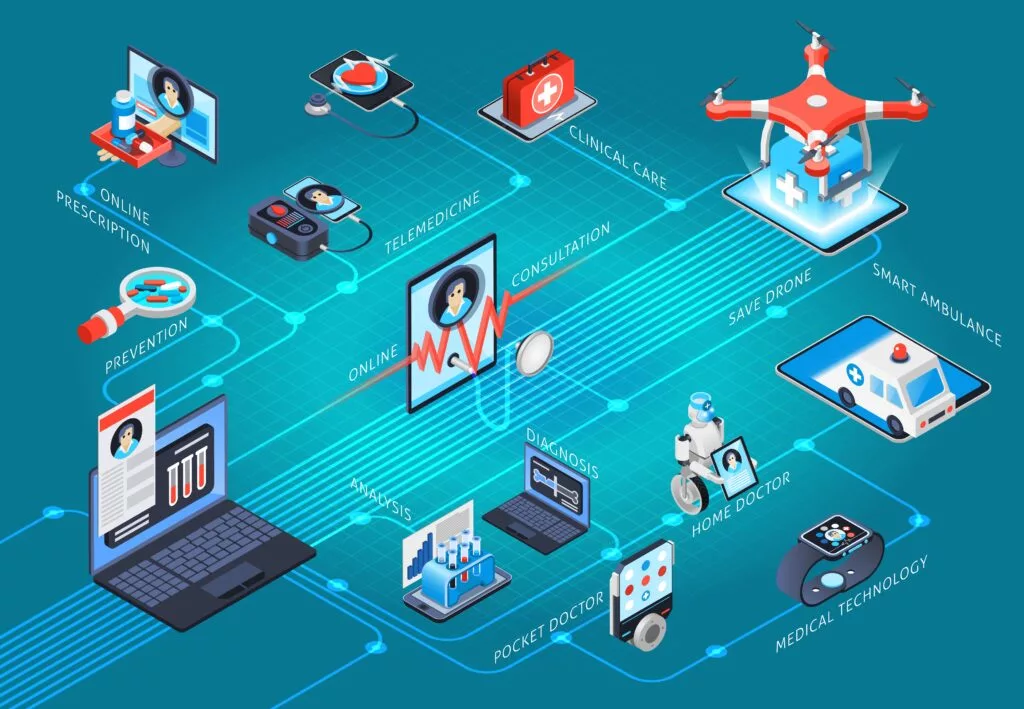
Telemedicine has become more accessible than ever before, thanks to advancements in communications and the Internet. Technological breakthroughs in data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and healthcare Internet of Things (IoT) have transformed the provision of healthcare services, paving the way for a revolution in the healthcare sector.
Patients will now get more customised clinical services. They can also meet the best medical providers simply by using video application software, consultations can be taken from afar, and clinicians have better-suited tools for networking, data storage, report management, and leveraging on each other’s specific skills. This improves the quality of medical practice, allowing doctors to spend less time on rural assignments and providing more care to patients. Telemedicine also enables private healthcare specialists to practise and will enhance the patient experience. Patients will no longer have to stand in long queues, and physicians will be able to access patient information more conveniently and efficiently with electronic files and eliminating overall wait times. Furthermore, remote appointments allow doctors to devote less time to each patient, allowing them to treat a more significant number of patients
Types of telemedicine
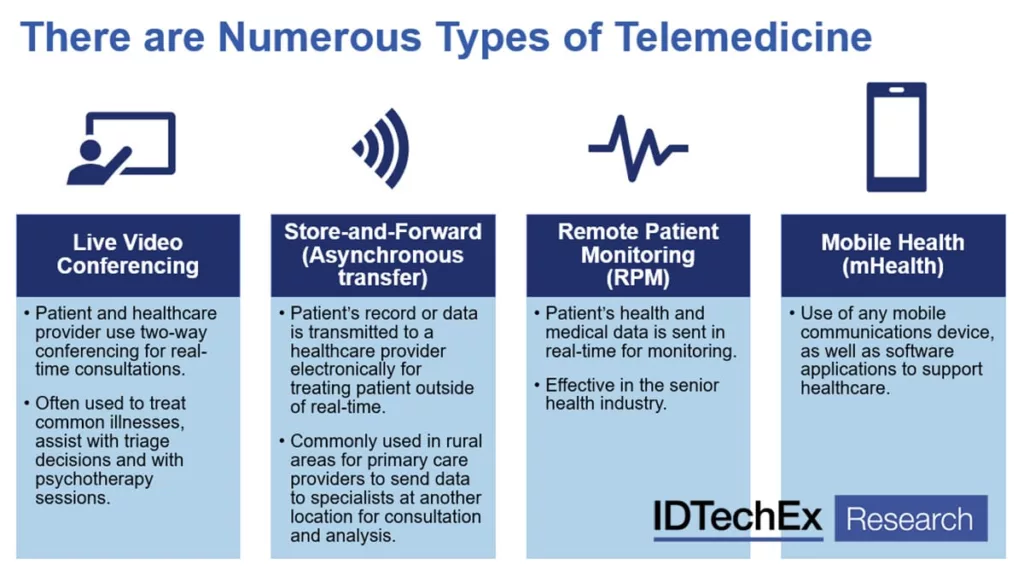
Telemedicine encompasses various approaches that enable remote healthcare delivery. Here are the main types of telemedicine:
1. Live video conferencing
This type of telemedicine involves real-time communication between healthcare providers and patients. It can be conducted through videoconferencing software or phone calls that comply with privacy regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Interactive telemedicine allows for virtual consultations, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring
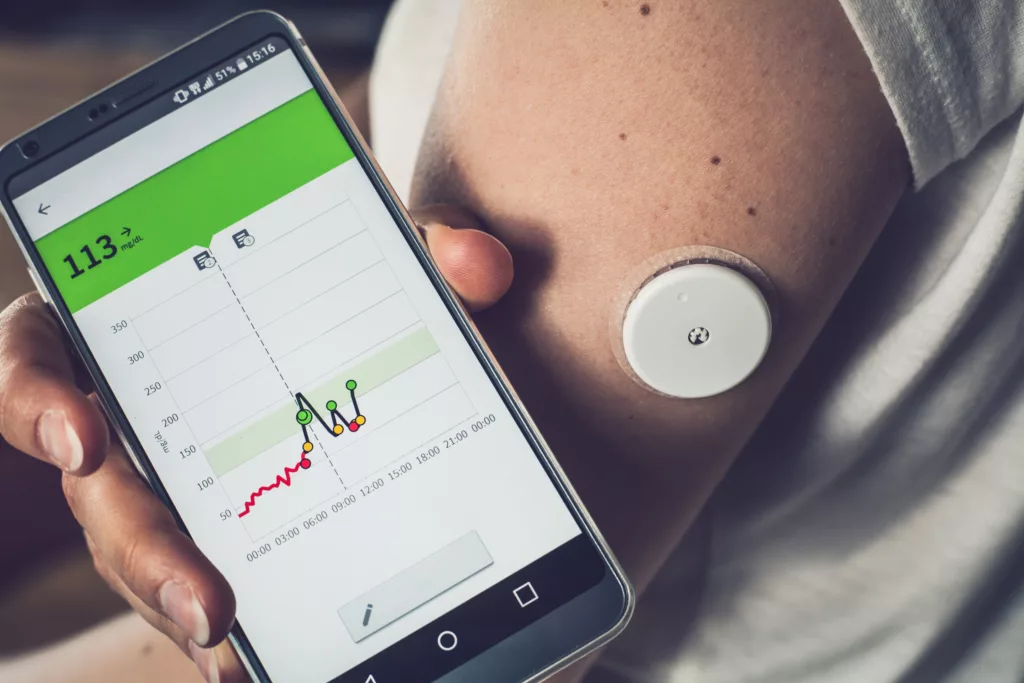

Woman checking glucose level with a remote sensor and mobile phone, sensor checkup glucose levels without blood. Diabetes treatment.
Remote patient monitoring involves the use of mobile health devices and applications to collect and transmit patient data from their home. Patients can monitor their vital signs, symptoms, and health conditions using wearable technology or specialized devices. This data is then transmitted to healthcare providers for remote monitoring and management of patients‘ health.
3. Store and Forward 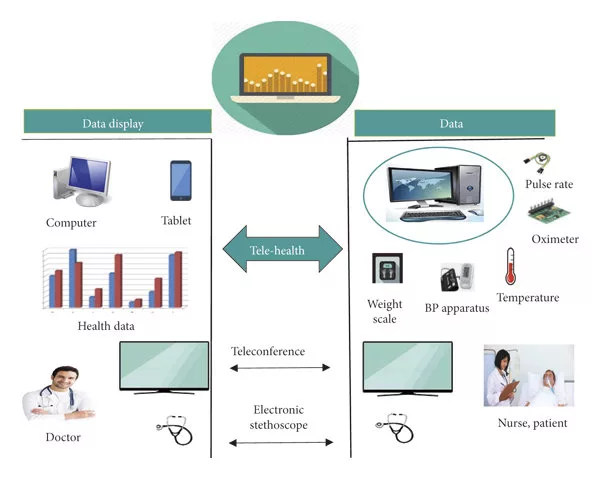 Also known as asynchronous telehealth, this approach involves the transmission of patient medical information, such as lab results, images, or diagnostic reports, from one healthcare provider to another. The information is securely shared electronically, enabling healthcare providers to review and assess the patient’s condition at a convenient time. This type of telemedicine is particularly useful for consultations with specialists or obtaining second opinions.
Also known as asynchronous telehealth, this approach involves the transmission of patient medical information, such as lab results, images, or diagnostic reports, from one healthcare provider to another. The information is securely shared electronically, enabling healthcare providers to review and assess the patient’s condition at a convenient time. This type of telemedicine is particularly useful for consultations with specialists or obtaining second opinions.
4. Mobile Telehealth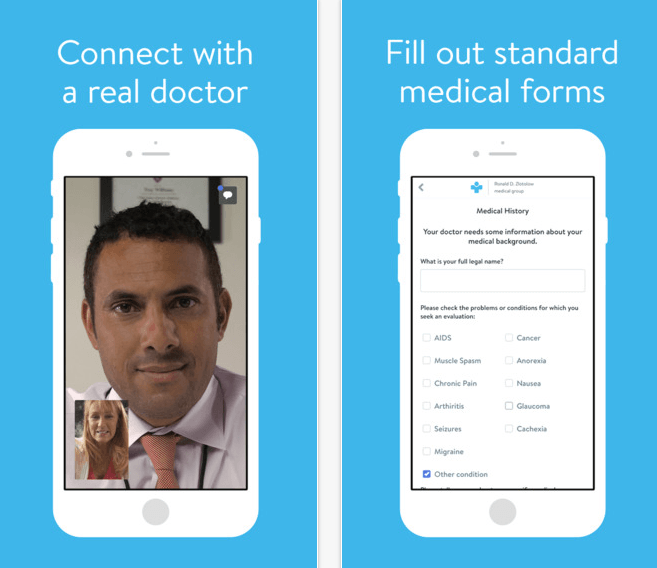
Mobile telehealth utilizes mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to deliver healthcare services. It includes remote clinical services, such as virtual consultations and patient-doctor communication through mobile patient portals. Mobile telehealth also encompasses public health activities, such as disseminating alerts and information about disease outbreaks or preventive measures through mobile apps.
These different types of telemedicine offer flexibility and convenience for both healthcare providers and patients. They enable timely access to care, remote monitoring of health conditions, secure sharing of medical information, and increased patient engagement. The adoption of telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare delivery by expanding access to quality care beyond traditional healthcare settings.
Why healthcare system needs telemedicine?
Rising healthcare expenditures and the demand for better treatment are prompting more hospitals to look at the benefits of telemedicine. They desire better contact between physicians and distant patients, as well as better utilisation of healthcare facilities. Telemedicine also encourages stronger connectedness in this setting, which has resulted in fewer hospital readmissions and patients completely following to their prescription treatment plans. The greater contact advantage of telemedicine extends to doctor-to-doctor communication as well. Doctors may use telemedicine to create support networks in order to share their knowledge and provide better healthcare services. Telemedicine is a method of providing medical treatment through the internet, typically via video chat. This technology offers numerous benefits to both patients and healthcare providers. Despite technical challenges and criticism, telemedicine can supplement and improve overall patient experience.
Telemedicine in healthcare: significant applications 
Telemedicine technology is being widely used in various areas of healthcare, offering significant benefits and convenience to both patients and healthcare providers. Some of the significant application areas of telemedicine include:
- Remote Visits for Chronic Conditions: Telehealth technology reduces the need for in-person visits, benefiting chronically ill patients and promoting adherence to treatment plans.
- Remote Monitoring: Healthcare teams can remotely monitor patients’ health using advanced technologies, enabling continuous tracking and early detection of any concerning changes.
- Wearable Devices: Innovative wearable devices facilitate seamless data transmission to healthcare providers, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis of vital signs and other health indicators.
- Home Monitoring Systems: These systems monitor key indicators such as blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and oxygen saturation. They also detect subtle changes in daily activities, enabling early identification of potential issues like falls or irregularities in routines.
- Telehealth for Medication Management: Telemedicine simplifies prescription renewals without the need for phone calls or in-person visits. It improves medication management, reduces hospital readmissions, and enhances medication compliance.
- Telemedicine for Follow-up Care: Telehealth enables easy compliance with follow-up care and appointments. Physicians can assess patients’ files and treatment responses virtually, intervening before costly hospital readmissions become necessary.
Telemedicine technology offers diverse applications that enhance patient care, increase accessibility, and improve health outcomes while reducing the need for unnecessary in-person visits.
Limitations of telemedicine
Any country that wants to improve the standard of healthcare, broaden access, and reduce costs should be investing in telemedicine technology. But it’s important to take into account obstacles like security worries, emergency suitability, technological issues, and the inability to get a proper medical exam.
One significant concern is the vulnerability of patient medical data to hacking, particularly when accessing telemedicine services from public networks or unencrypted channels. Additionally, in emergency situations, telemedicine can cause delays in delivering life-saving care or conducting necessary laboratory tests, as doctors are unable to provide immediate physical intervention remotely.
The rules and regulations governing telemedicine vary across states, which means physicians may be restricted from practicing medicine across state boundaries based on their licensure and the patient’s location. It is crucial for clinicians to ensure that the telemedicine services they employ are secure, reliable, and compliant with privacy laws.
During telemedicine sessions, healthcare providers heavily rely on patient self-reports, necessitating physicians to ask probing questions to obtain a comprehensive patient history. If a patient fails to disclose an important symptom that would have been detected during in-person care, it could potentially compromise the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
Availability and affordability are also significant drawbacks of telemedicine. The setup and management costs can be prohibitive for smaller healthcare facilities, making it less accessible to certain providers. Furthermore, inadequate communication channels may hinder the ability to provide reliable care, as clear and effective communication is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Embracing the Future of Telemedicine
In conclusion, telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare by improving accessibility, enhancing care quality, and reducing costs. Its wide range of applications, from chronic disease management to remote patient monitoring and medication management, makes it an invaluable tool in delivering comprehensive and patient-centered healthcare. As telemedicine continues to evolve and overcome its limitations, it holds immense potential for transforming the future of healthcare and improving health outcomes for individuals worldwide.
Partner with CMC Global for Cutting-Edge Telemedicine Solutions
Take a step into the future of healthcare with CMC Global’s telemedicine solutions. Contact us today to learn how our expertise and advanced technology can drive your telemedicine initiatives forward.