In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer. By harnessing the power of the cloud, healthcare organizations are revolutionizing how they store, access, and share medical data, streamline operations, and develop innovative telehealth solutions. This transformative technology not only improves the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services but also offers significant cost savings. With the global market value projected to exceed $89 billion by 2027 and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) experiencing exponential growth, it’s clear that cloud computing is reshaping the future of healthcare. Embracing the cloud opens a world of possibilities, enabling healthcare providers to deliver better care, enhance patient outcomes, and drive innovation in the industry.
In this article, we’ll provide a thorough understanding of cloud computing in healthcare, benefits and application of cloud computing in healthcare, deployment models, and why CMC Global can create the ideal healthcare cloud.
Cloud Computing Systems and Applications in Healthcare
Cloud-based healthcare refers to the use of cloud computing technology in the healthcare industry to store, manage, and access medical data and applications. It involves leveraging remote servers and networks hosted on the internet to store and process healthcare information securely.
In a cloud-based healthcare system, medical data, such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical images, lab results, and patient information, are stored in the cloud rather than on local servers or physical storage devices. Healthcare providers can access and share this information in real-time from any location and device with an internet connection, enabling seamless collaboration and enhancing patient care.
Research shows that cloud computing adoption in healthcare is on the rise. A survey conducted by HIMSS Analytics revealed that 83% of healthcare organizations are already utilizing cloud-based services. This trend is driven by the pressing need for secure data storage, seamless information exchange, and cost-effective solutions. However, challenges such as data privacy concerns and regulatory compliance need to be addressed to fully harness the potential of cloud computing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare offers benefits for both healthcare providers and patients. Healthcare providers use the cloud to lower costs and provide personalized medicine. On the other hand, with cloud adoption in healthcare, patients are getting faster delivery of healthcare services and are able to engage more with their care and treatment.
Some of the key benefits of cloud technology in healthcare:
- Cost savings: Cloud computing helps reduce costs by eliminating the need for expensive on-premises equipment and infrastructure. Healthcare providers can access the resources of cloud computing companies, pay for what they use, and eliminate the need for large in-house IT teams.
- Customization: Cloud-based solutions for healthcare are highly customizable, offering built-in care plans and features. With easy interfaces and templates, healthcare providers can tailor cloud-based solutions to their specific needs.
- High Data Storage Capacity: The cloud provides unlimited storage capacity, efficiently managing the increasing volume of digital data generated in healthcare. Healthcare organizations can store and manage medical records, prescriptions, lab tests, and other data without the need for expensive on-premises storage devices.
- Better Collaboration: Cloud computing enables safe and real-time data sharing among healthcare professionals, promoting collaboration and improved patient care. Remote conferencing and instant updates on patients’ conditions can be facilitated through the cloud, enhancing communication and coordination among care providers.
- Improved Patient Experience: Cloud computing enhances patient engagement by allowing them to access their medical information, prescriptions, and test results from anywhere, at any time. This empowers patients to be more involved in their own healthcare and improves their understanding of their medical conditions. Quick and secure data sharing through the cloud also reduces unnecessary testing and overprescription.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Challenges of cloud computing in healthcare include:
- Data Breach Risks: Despite stringent security measures, there is always a risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive healthcare information. Healthcare organizations must carefully select reputable and trustworthy cloud service providers and implement additional security measures to mitigate these risks.
- Reliance on Internet Connectivity: Cloud computing heavily relies on stable and reliable internet connectivity. If the internet connection is disrupted, healthcare providers may experience difficulties accessing patient data or providing real-time services. This dependency on internet connectivity can pose challenges in remote or underserved areas with limited access to high-speed internet.
- Vendor Dependency: Healthcare organizations become reliant on cloud service providers for the availability and performance of their cloud-based systems. In the event of service disruptions or vendor-related issues, healthcare providers may experience downtime or reduced system functionality, impacting patient care.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Healthcare organizations must navigate complex regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, when adopting cloud computing. They need to ensure that their chosen cloud service provider complies with these regulations to maintain the privacy and security of patient data.
- Data Migration and Integration Challenges: Transitioning existing systems and data to the cloud can be a complex and time-consuming process. Healthcare organizations may face challenges in migrating data from legacy systems, ensuring data integrity, and integrating cloud-based solutions with existing infrastructure.
Despite the challenges, the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare outweigh the disadvantages. With proper planning, robust security measures, and careful vendor selection, healthcare organizations can harness the power of cloud computing to drive innovation, improve patient care, and optimize operational efficiency.
Applications of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
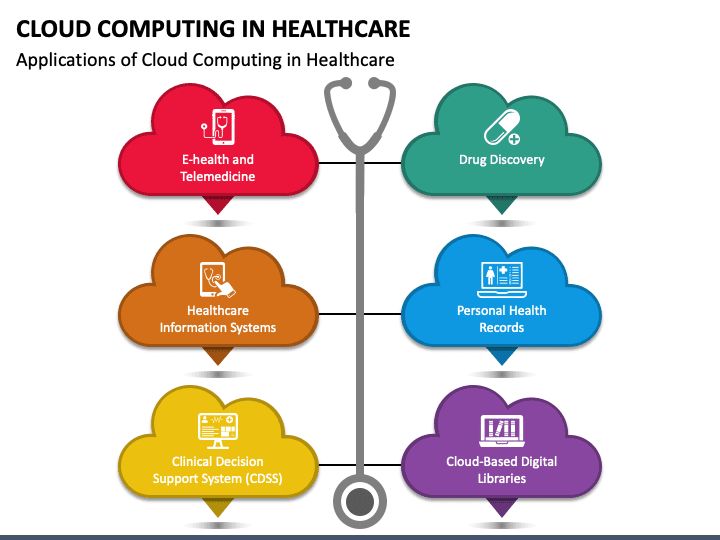
Cloud computing has revolutionized the healthcare industry, enabling the development and implementation of various applications that enhance patient care and improve operational efficiency. Here are some key applications of cloud computing in healthcare:
- E-Health and Telemedicine: Cloud-based platforms facilitate remote patient monitoring, teleconsultations, and telemedicine services, enabling healthcare professionals to provide timely care and consultations to patients regardless of their location.
- Clinical Decision Support System: Cloud-based clinical decision support systems leverage data analytics and machine learning algorithms to provide real-time insights and recommendations to healthcare professionals, assisting in accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions.
- Healthcare Information Systems: Cloud-based electronic health record (EHR) systems allow secure storage, retrieval, and sharing of patient data among authorized healthcare providers. This streamlines workflows, enhances collaboration, and improves patient outcomes.
- Drug Discovery: Cloud computing enables large-scale storage and processing of genomic and molecular data, accelerating the drug discovery process. Researchers can collaborate and analyze vast datasets to identify potential drug candidates more efficiently.
- Personal Health Record (PHR): Cloud-based PHR systems empower patients to access and manage their health information securely. They can track vital signs, manage appointments, and share their health records with healthcare providers, promoting patient engagement and personalized care.
- Cloud-Based Digital Libraries: Healthcare professionals can access comprehensive medical literature, research papers, and clinical guidelines through cloud-based digital libraries. This enables efficient knowledge sharing, staying updated with the latest advancements, and promoting evidence-based practices.
By leveraging cloud computing in these applications, healthcare organizations can improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and drive innovation. The scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of cloud solutions make them invaluable tools in the modern healthcare landscape.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing for the healthcare industry operates through two primary models: deployment and distribution. These models offer distinct approaches to utilizing cloud technology to enhance healthcare services. Let’s explore each model in more detail:
Deployment Model
The deployment model focuses on leveraging cloud infrastructure within a healthcare organization’s internal systems. In this approach, the healthcare provider utilizes cloud resources to enhance their existing infrastructure, such as data centers or private clouds. The key features of the deployment model include:
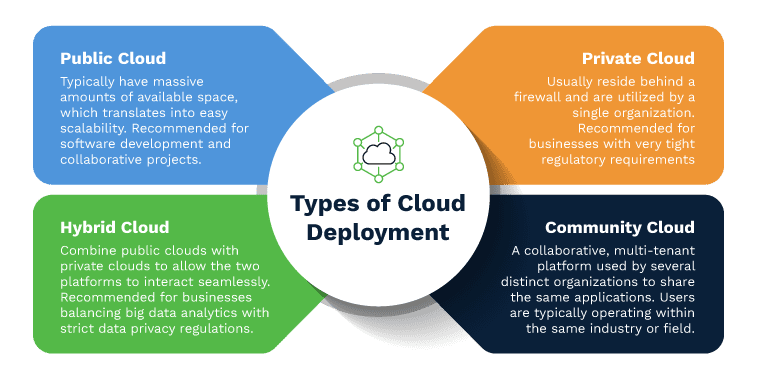
Private Cloud:
The healthcare organization builds and manages its own private cloud infrastructure, offering greater control, security, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Private clouds are particularly suitable for organizations with sensitive patient data or specific regulatory considerations.
Hybrid Cloud:
This model combines the use of private and public clouds, allowing healthcare organizations to enjoy the benefits of both environments. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, enabling organizations to leverage public cloud resources for non-sensitive data or peak workloads, while keeping sensitive data within a private cloud.
Community Cloud:
Community clouds are shared infrastructure environments that cater to multiple healthcare organizations, such as hospitals, clinics, or research institutions. These organizations collaborate to build and maintain cloud infrastructure, benefiting from shared resources, cost savings, and standardized processes.
Public Cloud:
Healthcare organizations leverage cloud services provided by third-party vendors, benefiting from their expertise and scalable infrastructure. A study published in the Journal of Medical Systems highlighted the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of public cloud solutions for healthcare data storage and analytics.
Distribution model:
The distribution model focuses on utilizing cloud computing to distribute healthcare services and applications to end-users, regardless of their location. With easy interfaces and templates, healthcare providers can tailor cloud-based solutions to their specific needs. The key features of the distribution model include:
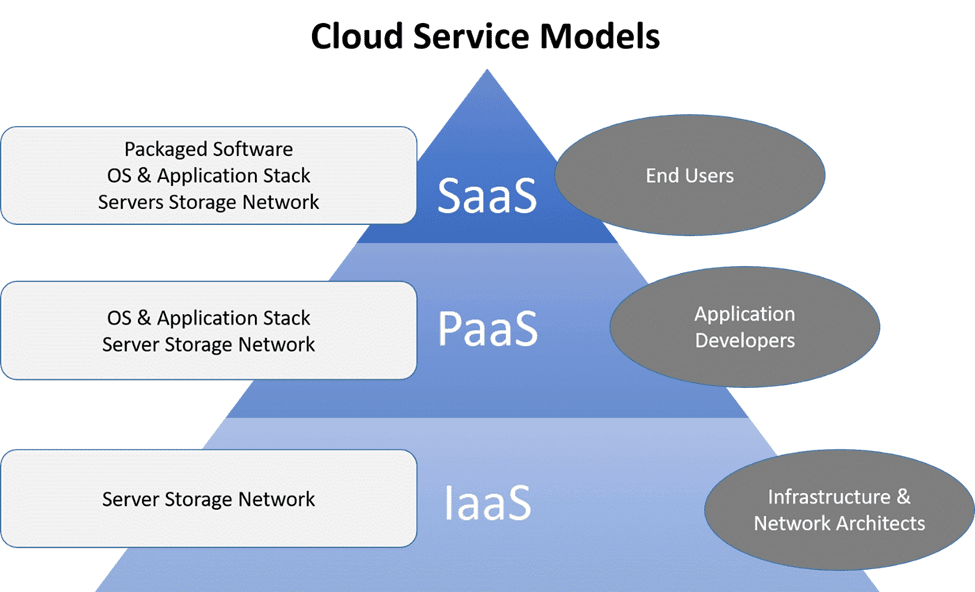
Software as a Service (SaaS):
Cloud-based applications, accessed through the internet, provide healthcare services to end-users. These applications eliminate the need for on-premises installations and allow healthcare providers to deliver services efficiently. Examples include telemedicine platforms, electronic health record systems, and patient engagement applications.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Cloud platforms provide healthcare organizations with the necessary infrastructure and tools to develop, deploy, and manage their own healthcare applications. PaaS enables healthcare providers to focus on application development and innovation without the burden of managing underlying infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Cloud infrastructure services offer virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking capabilities, to healthcare organizations. IaaS allows healthcare providers to rapidly scale their infrastructure, handle increased workloads, and optimize resource allocation.
Why choose CMC Global?
CMC Global is a member of CMC Corporation, providing information technology applications and digital transformation solutions such as cloud computing applications (Cloud), artificial intelligence (AI), and exporting software. Up to now, the company is the Advanced Tier Services Partner with AWS and has more than 100 AWS-certified engineers, with multiple companies supported by CMC Global to deploy AWS services successfully. CMC Global has already deployed various cloud computing projects successfully in general and conducted an Electronic Health Record System Development & Maintenance for a South Korea client. Discover our successful stories here: https://cmcglobal.com.vn/casestudies/healthcare/
Conclusion
The integration of cloud computing in healthcare represents a paradigm shift in the industry, unlocking new possibilities for improved patient care, operational efficiency, and data management. As healthcare organizations embrace the potential of cloud computing, they can deliver more accessible, collaborative, and patient-centric services. To leverage the power of cloud computing in healthcare, organizations can partner with CMC Global, an IT outsourcing company that specializes in providing tailored cloud computing solutions for the healthcare industry. Embrace the transformative capabilities of cloud computing and embark on a journey towards a more efficient, secure, and patient-centered healthcare ecosystem.





