The State of Data Security in Australia’s FinServ Industry
Data Governance and Security: Two Sides of the Same Coin
In the 2024 Data Threat Report by Thales, the percentage of FinServ organizations reporting a breach in the last 12 months decreased from 29% in 2021 to 14% in 2024.
According to Erick Reyes, ANZ Regional Director, Data Security for Thales, compliance achievements drive better security outcomes in financial services organizations accross Australia and New Zealand, leading to fewer breaches,
In detail, only 15% of fully compliant organizations had a breach history and just 3% experienced breaches in the last year.
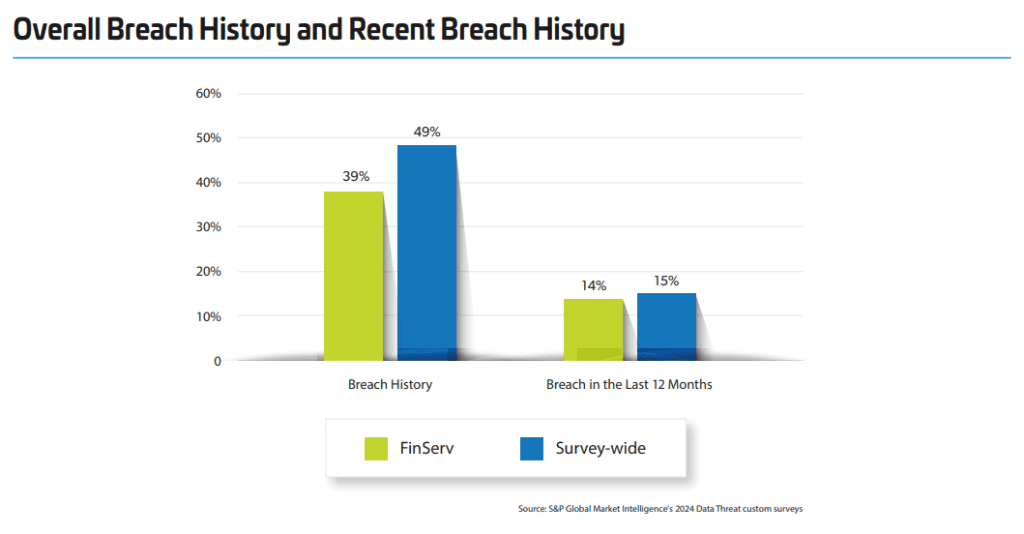
Despite these improvements, the preparedness for cyberattacks remains insufficient across the sector. Attack surfaces within and among FinServ organizations will continue to grow due to new technology adoption like AI, or quantum computing.
Alarmingly, only 25% have formulated a response plan to combat cybercrimes like ransomware, crypto jacking, or password attacks.
Key Data Management Priorities for CDOs to Strengthen Security
Beyond meeting regulatory requirements, CDOs must rethink their data strategy investments.
To reinforce data security, a recent IDC report revealed that data protection is the top priority for organizations, followed closely by enhancing metadata across data management systems, with cloud migration also ranking highly.
This is significant because metadata offers the intelligence needed to strengthen data protection, and modern technologies must be cloud-native to stay effective.
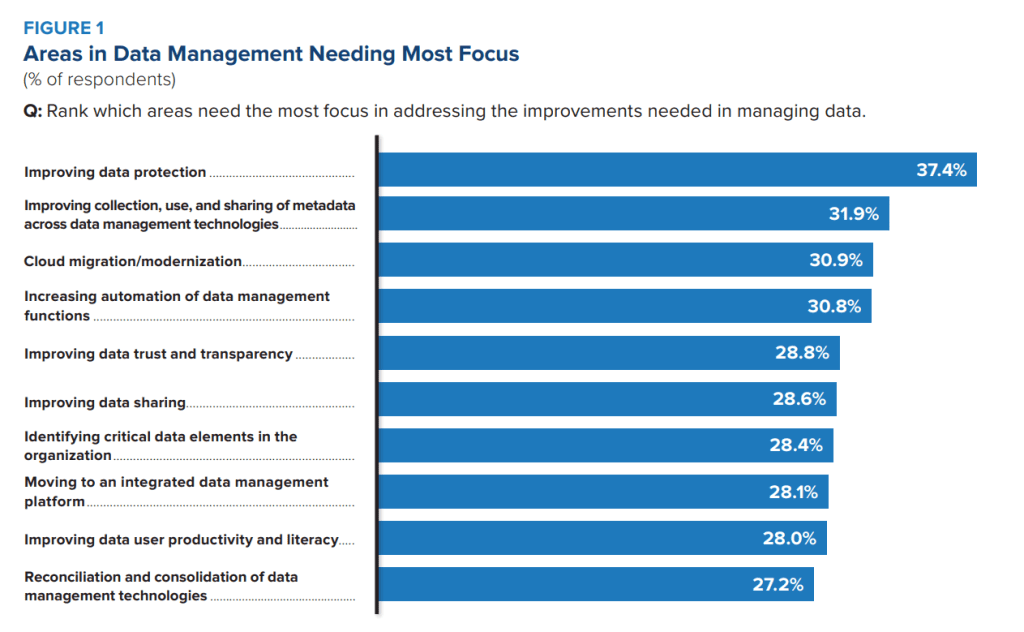
To proactively respond to a cyber incident, banking institutions need to start by implementing an active, metadata-driven system capable of effectively managing cybersecurity threats on cloud, while aligning with robust data governance standards
Metadata Management: Key To Data Security & Compliance

Metadata management is essential for data governance, allowing users to extract value from available data. It also helps business users classify data sets and identify sensitive information to ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Why Is Metadata Management Important?
Active metadata enables quicker and more scalable solutions for data security and governance, enhancing the speed and flexibility of the modern data stack.
Data Compliance
Metadata plays a key role in ensuring regulatory adherence and organized data management.
- Organizing Data: Metadata helps organize and make data interoperable, ensuring an up-to-date record of information.
- Regulatory Adherence: It aids in adherence to governmental policies and regulations by providing a clear audit trail and documentation for compliance checks.
Data Security
Metadata is vital for tracking data history, detecting security risks, and enforcing security policies.
- Tracking Data Lineage: Metadata provides detailed insights into the history, transformations, and usage of data, offering a comprehensive view of its entire lifecycle.
- Accurate Classification: It enables organizations to trace data lineage, helping to classify data accurately and identify elements that need protection.
- Anomaly Detection: Metadata-driven classification is critical for detecting and preventing anomalies or misuse that could compromise data security.
- Strengthening Policies: By leveraging metadata, organizations can develop stronger, more informed security policies and standards.
- Governance and Compliance: It ensures that data governance aligns with compliance
Gartner Market Guild On Active Metadata Management
Gartner predicts that, by 2026, organizations adopting active metadata practices will increase to 30%.
Following are 4 recommendations for evaluating metadata management solutions
- Use Flexible Metadata Solutions: Select tools that let you adjust settings like job flow and resource allocation easily, while also managing connections with third-party tools.
- Review Current Data Platforms: Check if your existing data platforms can share their internal metadata, which helps in connecting different systems smoothly.
- Switch to Active Metadata Tools: Choose tools that can both export their own metadata and import data from other sources, making your processing and optimization more efficient.
- Enable Automatic System Changes: Use tools that allow automatic updates in related data systems and support teamwork in managing metadata for better integration.
Guild To Data Protection Laws And Compliance For Australia Organizations
To achieve successful metadata management, banking institutions must cultivate a governance-driven data culture that prioritizes compliance with data protection laws.
Below are key Australian personal data protection laws that financial services organizations should be aware of:
The Privacy Act
- The Privacy Act 1988 with the latest update on 14 Oct 2024 is applied to most Australian organizations with an annual turnover of over $3 million, and certain small businesses.
- Key provisions of the Privacy Act include:
- Australian Privacy Principles (APPs): A set of 13 principles outlining how organizations must handle personal information.
- Data Breach Notification: Organizations must inform affected individuals and the OAIC of data breaches likely to cause serious harm.
- Cross-border Data Transfers: Organizations must ensure personal information is protected when transferred overseas.
Consumer Data Right (CDR)
- The Australian Consumer Data Right (CDR) gives consumers more control over their data, boosting competition in sectors like banking and finance.
- Following is the legal obligations for data recipients:
- Consent: Data can only be shared with the consumer’s explicit consent, with control over what is shared and for how long.
- Privacy Safeguards: 13 privacy safeguards ensure strict security and transparency in managing CDR data.
- CDR Policy: Accredited data recipients must have a clear, accessible CDR policy for consumers.
- Reporting: Data holders and recipients must submit reports to the ACCC every six months.
- IT requirements: Data holders must meet CDR’s IT, CX, and API standards.
Defence and Strategic Goods List (DGSL)
- The DSGL holds Australian-linked credit providers accountable for breaches of credit reporting laws, requiring both original data and copies to comply with privacy regulations.
State and Territory Privacy Laws
- In addition to federal privacy laws, some Australian states and territories have their own privacy laws.
- Information Privacy Act 2014 (Australian Capital Territory)
- Privacy and Data Protection Act 2014 (Victoria)
- Information Privacy Act 2009 (Queensland)
Improve your metadata management with CMC Global experts
CMC Global specializes in building metadata-driven systems that ensure robust governance and security, with a proven track record in the banking and financial services industry.
Here are what we focus on:
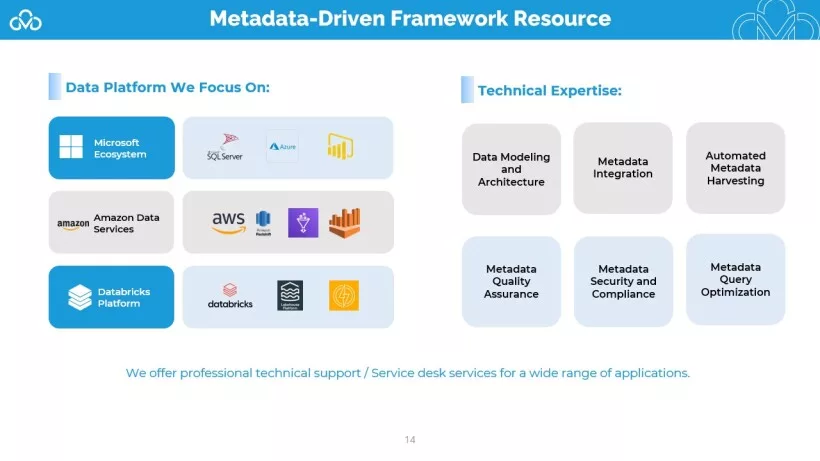
- Data Modeling and Architecture: Creates conceptual, logical, and physical data models, optimizing metadata for ETL and establishing standards for agile data architecture.
- Metadata Integration: Harmonizes metadata from legacy systems and cloud platforms, enhancing data lineage via middleware and ETL tools.
- Automated Metadata Harvesting: Uses advanced extraction tools, custom scripts, and AI to automate metadata tagging, categorization, and curation for big data analytics.
- Metadata Quality Assurance: Ensures accuracy through validation routines and continuous monitoring to maintain data lifecycle integrity.
- Metadata Security and Compliance: Aligns metadata management with GDPR and banking data protection standards.
- Metadata Query Optimization: Optimizes queries and tunes storage to improve performance, reduce latency, and support ad-hoc reporting.
We provide best practice guidance for metadata management to improve data quality and efficiency, integrating services from multiple vendors to address complex cybersecurity challenges and meet Australia’s data protection regulations.




