In business operation, cybersecurity is not just a requirement—it’s a foundation for trust and regulatory compliance. Adhering to cybersecurity guidelines while developing or offering services will help organizations safeguard sensitive data, mitigate risks, and meet industry standards.
In this blog, we’ll explore 5 cybersecurity best practices that Australia businesses should align with to maintain compliance and protect their operations from evolving threats.
Rising Cybersecurity Threats in Australia’s Open Banking Sector

From 2024 to early 2025, Australia experienced a surge in cybersecurity threats, particularly in the open banking sector.
In April 2024, a data breach at MediSecure compromised the medical records of approximately 12.9 million Australians. The following month, the Antidot Banker Trojan appeared, specifically targeting Android users of major Australian banking apps and putting their financial data at risk.
To enhance security, financial institutions have taken proactive steps. AMP, in partnership with Mastercard, is set to introduce Australia’s first numberless debit and credit cards, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
However, Australia continues to face advanced scams, resulting in significant financial losses. Therefore, the Australian Banking Association underscores the importance of customer awareness and proactive security measures, emphasizing the shared responsibility between banks and consumers in preventing cyber threats.
To navigate this evolving landscape, below are the top 5 cybersecurity practices Australian businesses should adopt to enhance resilience and protect sensitive data.
Top 5 Cybersecurity Practices For Australia Businesses
#1 ISO 27001/27002

The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develop globally recognized standards, including the ISO 27000 series, which sets the benchmark for information security management systems (ISMS).
Many leading financial institutions align with ISO 27001/27002 to strengthen their cybersecurity and data protection measures. Some major names in the finance sector that adhere to these standards include JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Goldman Sachs, Mastercard, Visa.
ISO 27001
As the core standard within the ISO 27000 series, ISO 27001 outlines the fundamental requirements for implementing an ISMS. It provides a structured approach to information security, making it an ideal starting point for organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Key steps in implementing ISO 27001 include:
- Forming a project team
- Conducting a gap analysis
- Defining the ISMS scope
- Developing security policies
- Performing risk assessments
- Implementing security controls
- Documenting risk management strategies
- Training employees on cybersecurity best practices
- Conducting internal audits and reviews
- Pursuing ISO 27001 certification (if required)
ISO 27002
Key focus areas include:
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Access control and authentication
- Managing third-party security risks
- Supplier relationship security
#2 Australian Government Information Security Manual

The Australian Government Information Security Manual (ISM), developed by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), provides a structured cybersecurity framework that organizations can integrate into their risk management strategies.
The ISM follows a six-step risk management framework:
- Define the system – Identify security objectives through risk assessment to evaluate potential threats to the system.
- Select controls – ACSC recommends tailored security controls to mitigate risks based on an organization’s specific cybersecurity needs.
- Implement controls – Recognizing that implementation may differ from planning, ACSC suggests documenting deviations in a security plan annex.
- Assess controls – ISM enables security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and areas for remediation.
- Authorize the system – Organizations must compile key security information, such as an incident response plan, continuous monitoring plan, and security assessment, to determine risk acceptability.
- Monitor the system – Ongoing, real-time monitoring ensures continued protection against cyber threats and security risks.
By following ISM’s four cybersecurity principles—Govern, Protect, Detect, and Respond—organizations can evaluate their security posture using a five-level maturity model.
#3 NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF)
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a division of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
The flexibility of NIST CSF makes it suitable for both small businesses with limited security measures and large enterprises with mature information security management systems. Whether an organization is just starting or refining its cybersecurity policies, NIST provides a scalable and industry-aligned framework.
Major corporations, including Bank of America, JPMorgan Chase, and Intel, integrate NIST CSF into their security programs.
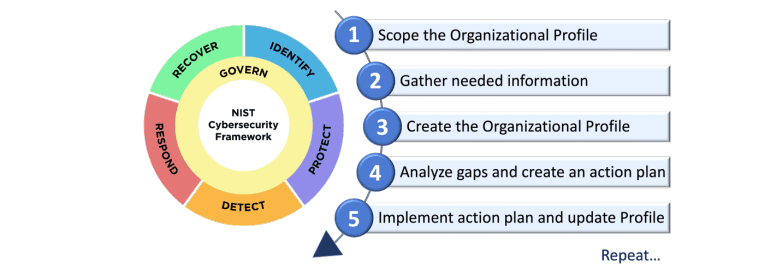
Source: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.29.pdf
Five Core Functions of NIST CSF
- Identify – Understand and manage cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities.
- Protect – Implement safeguards to ensure critical infrastructure resilience.
- Detect – Develop mechanisms to recognize cybersecurity incidents.
- Respond – Establish an effective response strategy to minimize the impact of cyber incidents.
- Recover – Implement plans for system restoration and resilience after an attack.
#4 GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in 2016, was designed to enhance data protection standards for European Union (EU) citizens. It applies not only to organizations based in the EU but also to any business—regardless of location—that collects or stores the personal data of EU citizens.
This regulatory framework consists of 99 articles outlining compliance obligations, such as individuals’ rights to access their data, requirements for data protection policies, and strict breach notification rules.
Several major financial institutions align with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to ensure data privacy and compliance with EU regulations. Some well-known names include JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Goldman Sachs, and Deutsche Bank.
#5 SOC2
Service Organization Control (SOC) Type 2 is a trust-driven cybersecurity framework and audit standard created by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to assess how securely vendors and partners handle client data.
SOC 2 outlines over 60 compliance requirements and detailed auditing processes for evaluating third-party systems and controls. Due to its thoroughness, SOC 2 is considered one of the most challenging security frameworks to implement, particularly for financial and banking organizations that must meet stricter compliance standards.
How CMC Global Supports Businesses in Cybersecurity Framework Implementation
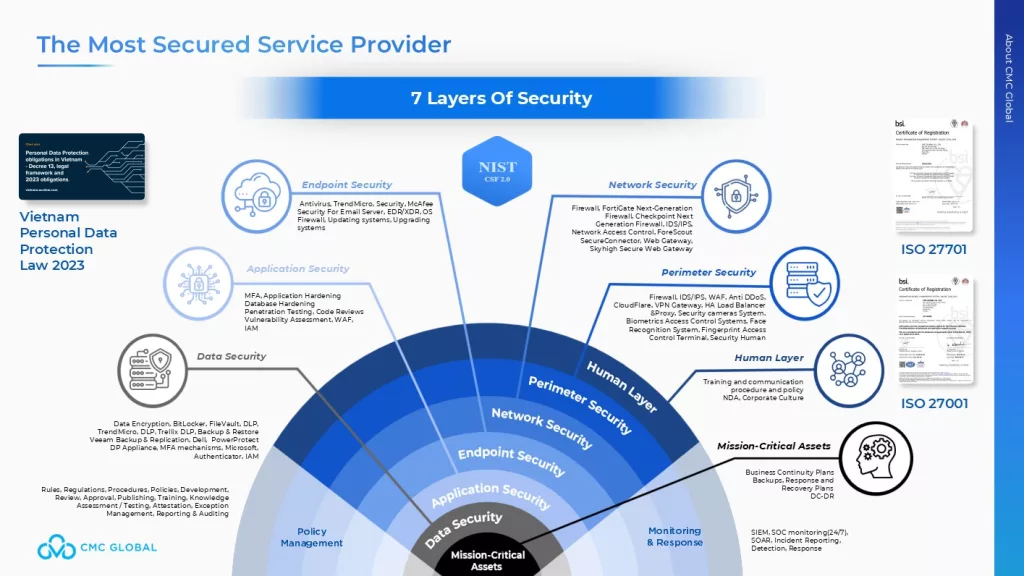
Businesses partnering with CMC Global benefit from a security-first approach that ensures compliance with industry standards. Through expert consulting services, CMC Global helps businesses navigate cybersecurity regulations like ISO 27001, ISO 27701, NIST CSF 2.0 with 7 layers of security: Human layer, Perimeter security, Network security, Endpoint security, Application security, Data security, Mission-critical assets.
Additionally, CMC Global fosters a highly skilled cybersecurity team, encouraging professionals to obtain top industry certifications such as Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP).
This commitment to compliance and expertise strengthens businesses’ security posture, mitigating risks and ensuring regulatory alignment.
Contact us today to learn more about how CMC Global can support your cybersecurity strategy!




